Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Potential Difference, Ohm's Law, Resistance, Resistance of a Wire, Resistivity, Electric Current Density and Ohm's Law in Vector Form.
Important Questions on Ohm's Law
A wire of resistance is gradually stretched to double its original length. It is then cut into two equal parts. These parts are then connected in parallel across a battery. Find the current drawn from the battery.
A physical quantity, associated with electrical conductivity, has the SI unit ohm-meter. Identify this physical quantity.
A voltage of is applied across a carbon resistor with first, second and third rings of blue, black and yellow colours respectively. Calculate the value of current, in , through the resistor.
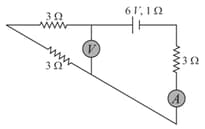
In the circuit diagram shown below, and are the potentials at points and respectively. Then. is
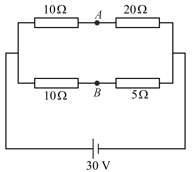
The terminal potential difference across and in the circuit shown is
Ends of two wires and having resistivity and of same cross section area joined in series together to from a single wire. If the resistance of the joined wire does not change with temperature, then find the ratio of their lengths , given that temperature coefficient of resistivity of wire and is and . Assume that mechanical dimensions do not change with temperature
A cylindrical conductor of length and inner radius and outer radius has specific resistance . A cell of emf is connected across the two lateral faces of the conductor. Find the current from the cell.
The relationship between the current density and the electric field is given by equivalently represents
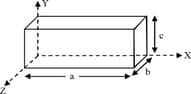
A solid metallic cuboid of homogeneous material having geometrical dimension as shown in the figure will have a ratio of resistances for the sense of current along , and directions respectively, equal to
Current is flowing with a current density in a copper wire. Assuming that each copper atom contributes one free electron and given that
Avogadro number
Density of copper
Atomic weight of copper
The drift velocity of electrons is
A current of is established in a circuit containing an aluminium resistor of length . If the area of cross-section of the resistor is at a point P.The current density at that point will be :
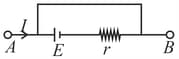
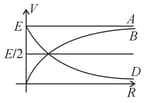
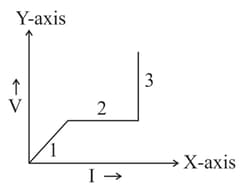
A cell of emf having an internal resistance is connected to an external resistance . The potential difference across the resistance varies with as shown by the curve,
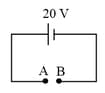
In the shown circuit, what is the potential difference across and ?
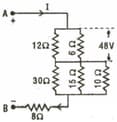
In the figure the potential difference across resistor is . Then the potential difference between and is
A steady current is set up in a wire whose cross-sectional area decreases in the direction of the flow of the current. Then, as we examine the narrowing region
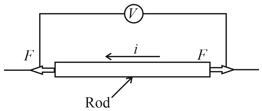
As shown in the schematic below, a rod of uniform cross-sectional area and length is carrying a constant current through it and voltage across the rod is measured using an ideal voltmeter. The rod is stretched by the application of a force .
Which of the following graphs would show the variation in the voltage across the rod as function of the strain when the strain is small. Neglect Joule heating.
Two metal slabs of equal lengths, equal cross sectional areas and having resistances in the ratio are connected first in series and then in parallel separately. The ratio of their effective conductivities is
A graph drawn between current and voltage in a conductor is as shown in the figure. The changes in the resistance in and parts respectively
A cylindrical conductor has a uniform cross-section. The resistivity of its material increases linearly from left end to right end. If a constant current is flowing through it and at a section distance from left end, the magnitude of electric field intensity is , which of the following graphs is correct?
In the given circuit ammeter and voltmeter are ideal and battery of has internal resistance . The reading of voltmeter and ammeter is